Difference Between CT and PET CT: Understanding the Distinctions
Guide or Summary:Computerized Tomography (CT)Positron Emission Tomography (PET)Difference Between CT and PET CTBenefits of Each Imaging ModalityWhen to Use……
Guide or Summary:
- Computerized Tomography (CT)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Difference Between CT and PET CT
- Benefits of Each Imaging Modality
- When to Use CT and PET CT Imaging
- FAQs
- Difference Between CT and PET CT: Understanding the Distinctions
- What are the risks associated with CT and PET CT imaging?
- What are the benefits of using both CT and PET CT imaging?
Computerized Tomography (CT)
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Difference Between CT and PET CT
Benefits of Each Imaging Modality
When to Use CT and PET CT Imaging
FAQs
Difference Between CT and PET CT: Understanding the Distinctions
Computerized Tomography (CT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) are two of the most advanced imaging techniques used in modern medicine. While they both provide detailed images of the body's internal structures, they differ in how they create these images and what they reveal about a patient's condition. Understanding the differences between CT and PET CT is essential for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Computerized Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves through a donut-shaped scanner, while the X-ray tube rotates around the patient, emitting X-rays from multiple angles. These X-rays are then detected by a series of detectors that create a detailed image of the body's interior. CT scans are commonly used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including fractures, tumors, and infections.
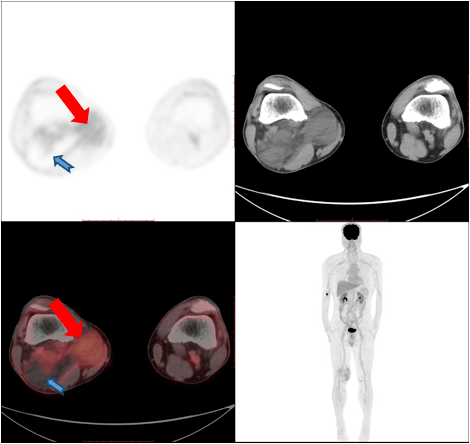
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is another advanced imaging technique that uses radioactive substances to create detailed images of the body's internal structures. During a PET scan, a small amount of a radioactive substance, such as fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), is injected into the patient's bloodstream. This substance is then absorbed by cells that are actively dividing or using glucose for energy. A PET scanner detects the radiation emitted by these cells, creating a detailed image of the body's internal structures. PET scans are commonly used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
The main difference between CT and PET CT is how they create images. CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body, while PET scans use radioactive substances to create images that reflect the body's metabolic activity. Because of this difference, CT and PET CT imaging are used for different purposes. CT scans are commonly used to diagnose structural abnormalities, such as fractures and tumors, while PET scans are commonly used to diagnose metabolic abnormalities, such as cancer and heart disease.
Both CT and PET CT imaging have numerous benefits. CT scans are fast, non-invasive, and can provide detailed images of the body's interior. They are also relatively inexpensive and widely available. PET scans, on the other hand, provide a more detailed look at the body's metabolic activity, which can be useful in diagnosing conditions that are difficult to diagnose with CT scans alone. They are also highly accurate and can provide valuable information about the extent and progression of a disease.
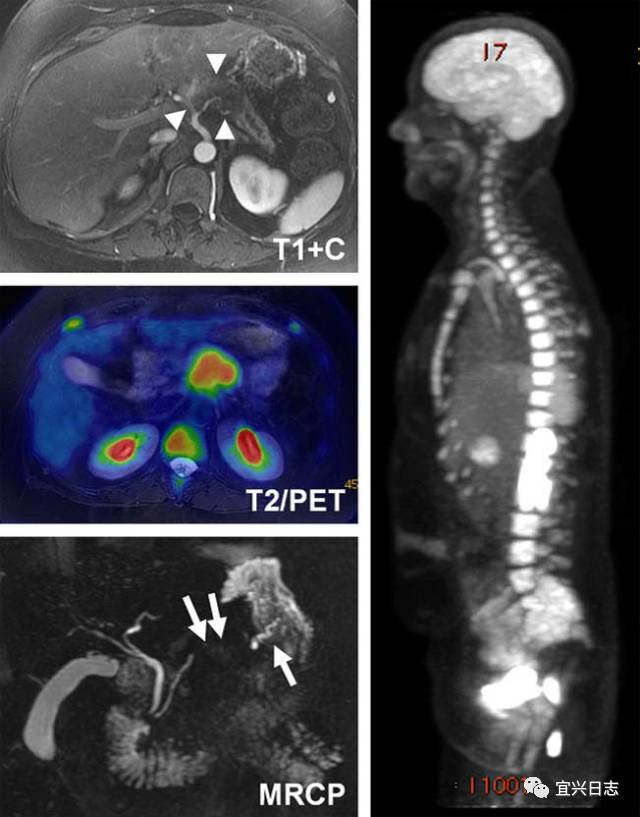
The decision to use CT or PET CT imaging depends on the specific condition being investigated. CT scans are commonly used to diagnose conditions such as fractures, tumors, and infections. They are also useful for evaluating the effects of treatment and monitoring the progression of certain conditions. PET scans, on the other hand, are commonly used to diagnose conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. They are also useful for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and monitoring the progression of certain conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between CT and PET CT imaging is essential for patients and healthcare professionals alike. While both imaging techniques provide valuable information about the body's internal structures, they differ in how they create images and what they reveal about a patient's condition. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each imaging modality, patients and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about which imaging technique to use for a specific condition.
What are the risks associated with CT and PET CT imaging?
CT scans expose patients to a small amount of ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer over time. PET scans also expose patients to a small amount of ionizing radiation, but the amount is generally lower than that used in CT scans. Patients with a history of cancer or other conditions that increase their sensitivity to radiation should discuss the risks and benefits of CT and PET CT imaging with their healthcare provider.

What are the benefits of using both CT and PET CT imaging?
Using both CT and PET CT imaging can provide a more comprehensive view of a patient's condition. CT scans provide detailed images of the body's structure, while PET scans provide detailed information about the body's metabolic activity. By combining the results of both imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can make more accurate diagnoses and develop more effective treatment plans.